Questions: Is there an association between a new school policy and the position a person holds within the school? A single stratified random sample of students, teachers, and administrators (principals and team leaders) from the school population was The p-value for a chi-square test for independence on this association is = ?
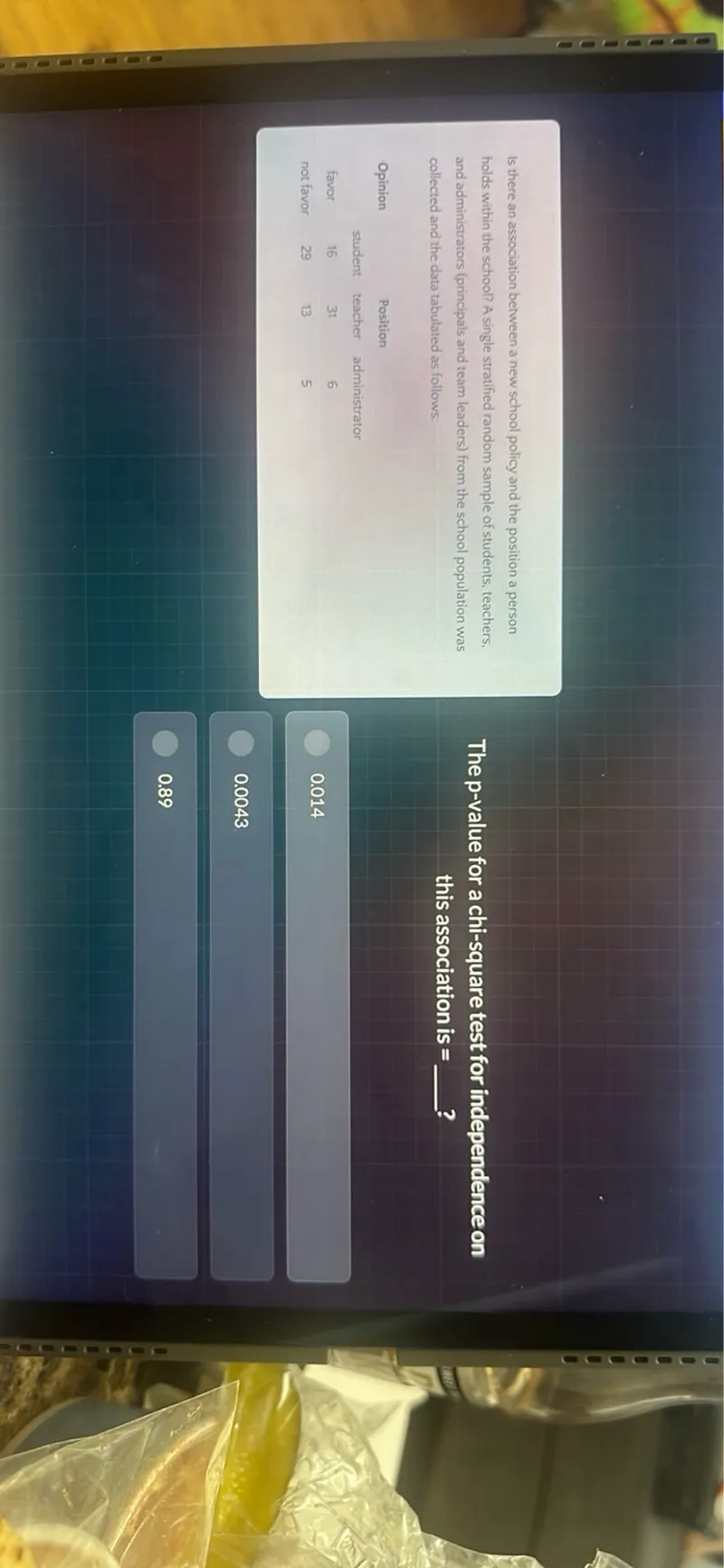
Transcript text: Is there an association between a new school policy and the position a person
holds within the school? A single stratified random sample of students, teachers,
and administrators (principals and team leaders) from the school population was
The $p$-value for a chi-square test for independence on
this association is = __?





