Questions: Solve the system of linear equations, using the Gauss-Jordan elimination method. (If there is n in terms of the parameters t and/or s.) x-2 y=3 7 x-14 y=21 3 x-6 y=9 (x, y)=(0,-3/2)
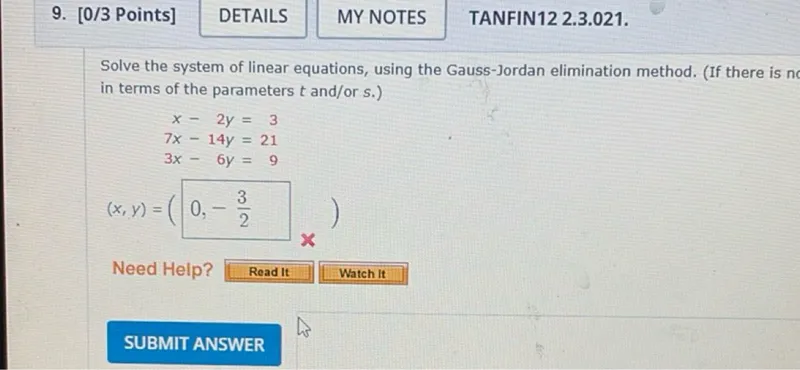
Transcript text: Solve the system of linear equations, using the Gauss-Jordan elimination method. (If there is $n$ in terms of the parameters $t$ and/or s.)
\[
\begin{array}{c}
x-2 y=3 \\
7 x-14 y=21 \\
3 x-6 y=9 \\
(x, y)=\left(0,-\frac{3}{2}\right)
\end{array}
\]





