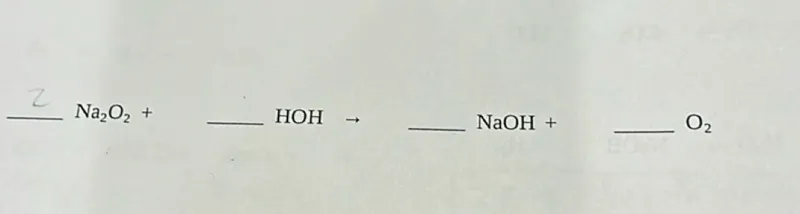The given chemical equation is:
_ Na₂O₂ + _ HOH → _ NaOH + _ O₂
This represents the reaction of sodium peroxide (Na₂O₂) with water (HOH, which is the same as H₂O) to produce sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and oxygen gas (O₂).
There are 2 Na atoms on the reactant side and 1 Na atom on the product side. To balance the Na atoms, we put a coefficient of 2 in front of NaOH:
_ Na₂O₂ + _ HOH → 2 NaOH + _ O₂
Now there are 2 H atoms on the reactant side and 2 H atoms on the product side (from the 2 NaOH). So, hydrogen is balanced.
There are 2 O atoms from Na₂O₂ and 1 O atom from HOH, totaling 3 O atoms on the reactant side. On the product side, there are 2 O atoms from 2 NaOH molecules, and 2 from the O₂. Thus, there are 4 oxygen atoms on the product side, and 3 oxygen atoms on the reactant side.
To balance the oxygen atoms, we modify the whole equation. Since oxygen is diatomic as O₂, we'll work around even numbers. Since the reactant side has an odd number of oxygens, let's multiply the number of NaOH by 2:
_ Na₂O₂ + _ HOH → 4 NaOH + _ O₂
Now there are 4 oxygens from 4 NaOH. We can't change O₂. To get the sodium to balance again, we multiply the number of Na₂O₂ molecules by 2:
2 Na₂O₂ + _ HOH → 4 NaOH + _ O₂
Now there are 6 oxygen atoms on the reactant side (4 from 2 Na₂O₂ and 2 from HOH or 2H₂O). Since there are 4 oxygen atoms from 4NaOH, the oxygen from O₂ has a coefficient of 1.
Then, we must increase the amount of water molecules to balance the oxygen.
2 Na₂O₂ + 2 HOH → 4 NaOH + O₂
Now, there are 6 oxygens on the reactant side and 6 oxygens on the product side.
\( \boxed{2 Na_2O_2 + 2 H_2O \rightarrow 4 NaOH + O_2} \)