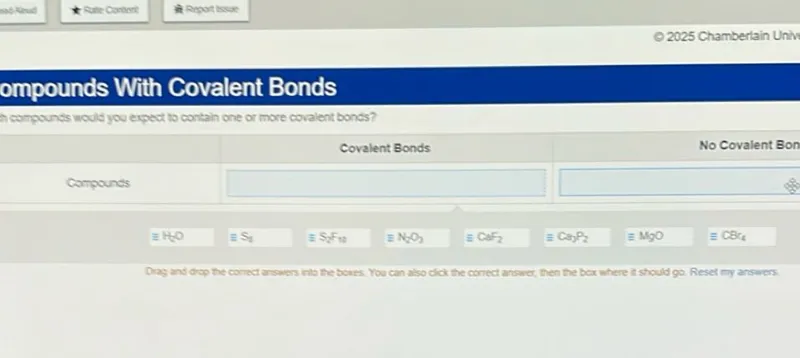
Determine which compounds contain one or more covalent bonds by analyzing their chemical composition and bonding patterns.
Understanding covalent bonding
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This typically occurs between:
- Two nonmetals
- A nonmetal and a metalloid
- Sometimes in polyatomic ions
Ionic bonds, in contrast, form between metals and nonmetals through electron transfer.
Analyzing each compound
Let's examine each compound:
H₅O: Hydrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals. This would form covalent bonds, though H₅O is not a stable compound (likely H₃O⁺ with water).
S₂: Sulfur is a nonmetal. Two sulfur atoms would form covalent bonds with each other.
S₂F₃₀: Sulfur and fluorine are both nonmetals. They would form covalent bonds.
N₂O₃: Nitrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals. They would form covalent bonds.
CaF₂: Calcium is a metal and fluorine is a nonmetal. This forms ionic bonds.
Ca₃P₂: Calcium is a metal and phosphorus is a nonmetal. This forms ionic bonds.
MgO: Magnesium is a metal and oxygen is a nonmetal. This forms ionic bonds.
CSr₄: Carbon is a nonmetal and strontium is a metal. This would have both ionic character (between Sr and C) and potentially some covalent character.
Categorizing the compounds
Compounds with covalent bonds:
- H₅O (though not a standard compound)
- S₂
- S₂F₃₀
- N₂O₃
- CSr₄ (likely has some covalent character)
Compounds with no covalent bonds (purely ionic):
\(\boxed{\text{Compounds with covalent bonds: H₅O, S₂, S₂F₃₀, N₂O₃, CSr₄}}\)
\(\boxed{\text{Compounds with covalent bonds: H₅O, S₂, S₂F₃₀, N₂O₃, CSr₄}}\)
\(\boxed{\text{Compounds with no covalent bonds: CaF₂, Ca₃P₂, MgO}}\)