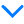
Questions: 1a. On what open intervals is f(x) increasing? -3<x<3 1b. On what open intervals is f(x) concave down? 0<x<0.5 1c. On what interval is the rate of change of f(x) negative and decreasing? -6<x<-3

Transcript text: 1.
1a. On what open intervals is $f(x)$ increasing?
\[
-3
Solution
Notification
Thank you for your feedback.
Notification
Copied!





