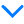
Questions: d. P(z ≥ -2.5) e. P(-3 < z ≤ 0)

Transcript text: d. $P(z \geq-2.5)$
e. $P(-3
Solution
Notification
Thank you for your feedback.
Notification
Copied!





