Questions: Attempt 1:5 attempts remaining. Consider the function, g(x)=x^2-2x. Complete the table below, then estimate the instantaneous rate of change of the function g at x=4. Fixed Endpoint Other Endpoint Δx Slope of Secant Line (Average Rate of Change) ------------ (4,8) (3.9,7.41) 0.1 5.9 (4,8) (3.99,7.9401) 0.01 (4,8) (3.999,7.994) 0.001 5.999 (4,8) (3.9999,7.9994) 0.0001 (4,8) (4.1,8.61) -0.1 6.1 (4,8) (4.01,8.0601) -0.01 6.01 (4,8) (4.001,8.006) -0.001 (4,8) (4.0001,8.0006) -0.0001 Estimate of the instantaneous rate of change of the function g at x=4 :
Transcript text: Attempt 1:5 attempts remaining.
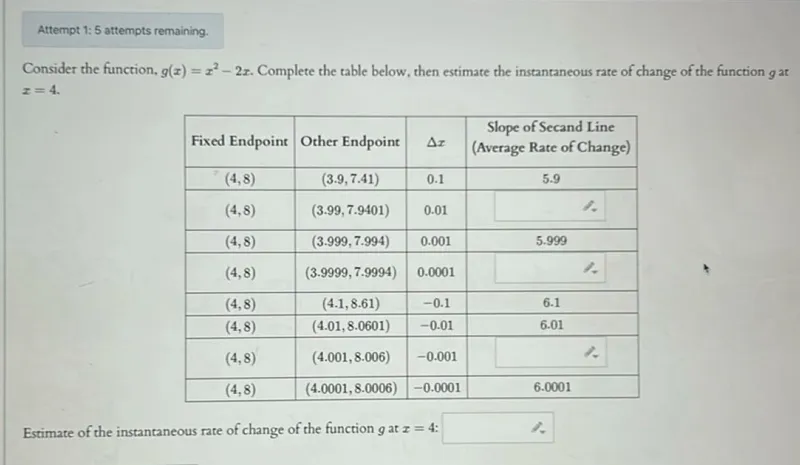
Consider the function, $g(x)=x^{2}-2 x$. Complete the table below, then estimate the instantaneous rate of change of the function $g$ at $x=4$.
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline Fixed Endpoint & Other Endpoint & $\Delta x$ & \begin{tabular}{c}
Slope of Secand Line \\
(Average Rate of Change)
\end{tabular} \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(3.9,7.41)$ & 0.1 & 5.9 \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(3.99,7.9401)$ & 0.01 & \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(3.999,7.994)$ & 0.001 & 5.999 \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(3.9999,7.9994)$ & 0.0001 & \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(4.1,8.61)$ & -0.1 & 6.1 \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(4.01,8.0601)$ & -0.01 & 6.01 \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(4.001,8.006)$ & -0.001 & \\
\hline$(4,8)$ & $(4.0001,8.0006)$ & -0.0001 & \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
Estimate of the instantaneous rate of change of the function $g$ at $x=4$ :





