Questions: Find the exact value of cos^(-1)(-(sqrt(3)/2)). cos^(-1)(-(sqrt(3)/2))=-(pi/3) cos^(-1)(-(sqrt(3)/2))=(5pi/6) cos^(-1)(-(sqrt(3)/2))=-(pi/6) cos^(-1)(-(sqrt(3)/2))=(2pi/3)
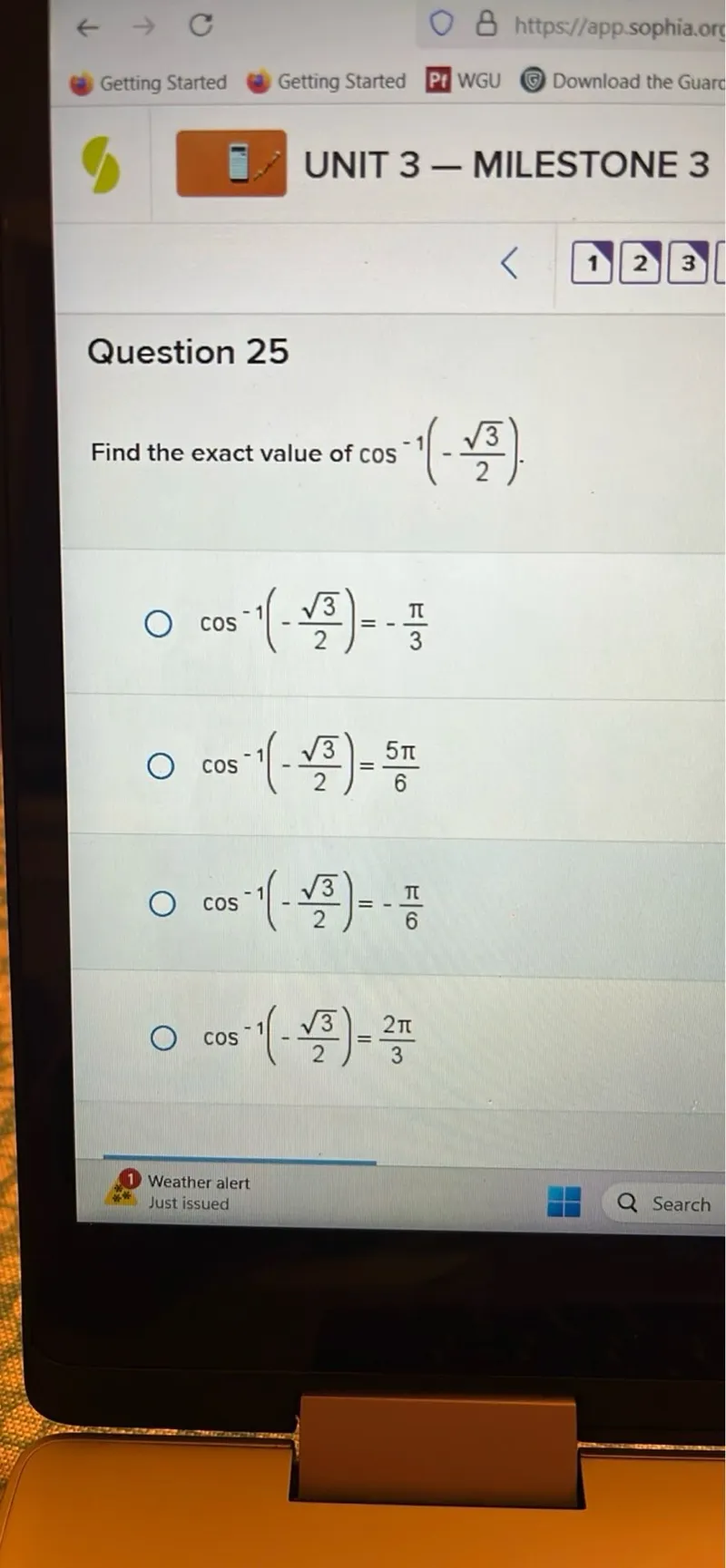
Transcript text: Find the exact value of $\cos ^{-1}\left(-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)$.
$\cos ^{-1}\left(-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)=-\frac{\pi}{3}$
$\cos ^{-1}\left(-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)=\frac{5 \pi}{6}$
$\cos ^{-1}\left(-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)=-\frac{\pi}{6}$
$\cos ^{-1}\left(-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)=\frac{2 \pi}{3}$





