Questions: Virtual Lab 0 - ALEKS Tutorial ALEKS - Leah Pons - Knowledge - www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1ou-IgNsIkr7j8P3jH Initial Knowledge Check Question 1 Count the significant digits in each of these measurements: measurement number of significant digits ------ 5.5 × 10^-1 mL 17700 kg 0.006700 J -6.0 × 10^-3 kJ / mol IDon't Know Submit Feels colder Now Search
Transcript text: Virtual Lab 0 - ALEKS Tutorial
ALEKS - Leah Pons - Knowledge
- www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNsIkr7j8P3jH
Initial Knowledge Check
Question 1
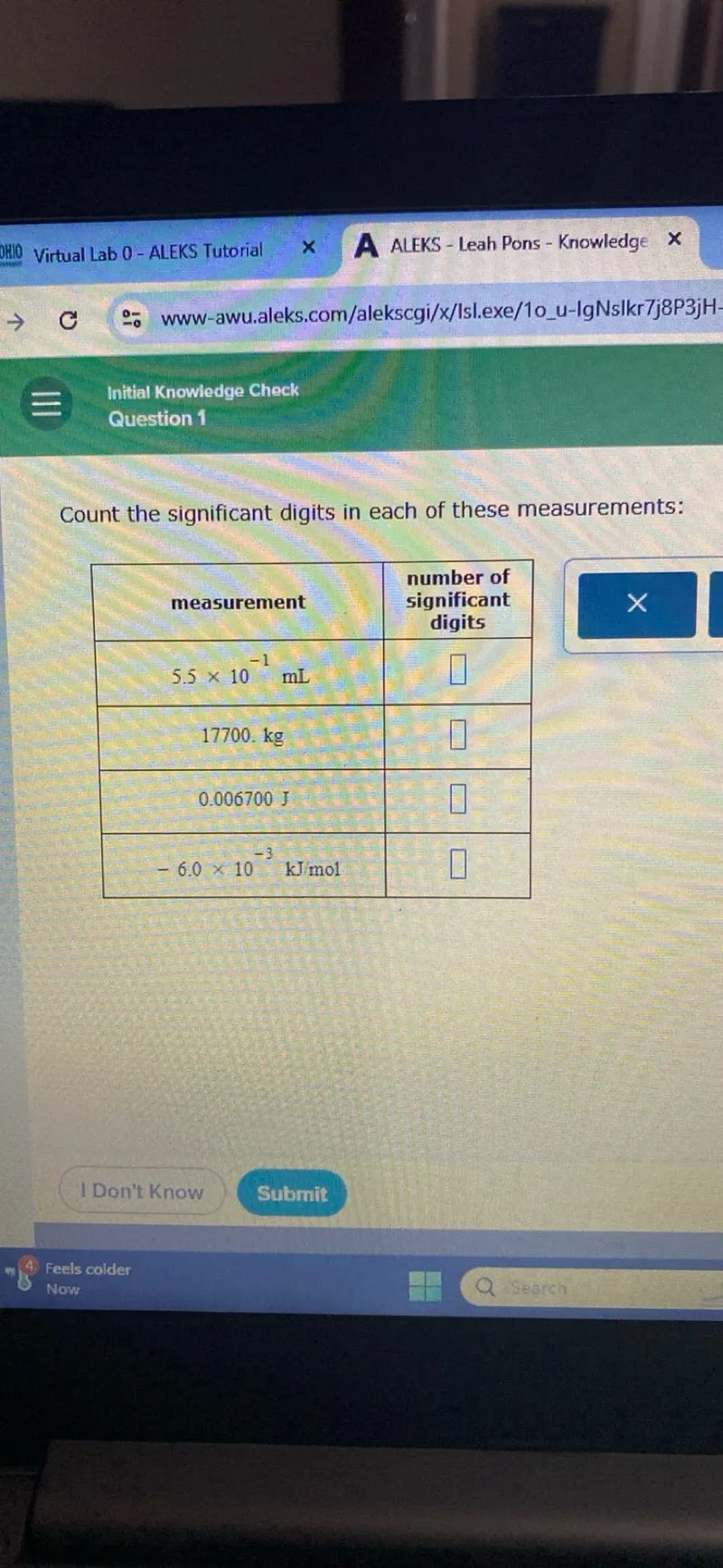
Count the significant digits in each of these measurements:
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline measurement & \begin{tabular}{c}
number of \\
significant \\
digits
\end{tabular} \\
\hline $5.5 \times 10^{-1} \mathrm{~mL}$ & $\square$ \\
\hline $17700 . \mathrm{kg}$ & $\square$ \\
\hline 0.006700 J & $\square$ \\
\hline$-6.0 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol}$ & $\square$ \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
IDon't Know
Submit
Feels colder
Now
Search





