Questions: Suppose that at first, Rajiv charges the same price of 8 per admission in both markets so that the total number of admissions demanded is 9 tickets. Suppose now that Rajiv decides to charge a different price in each market. To maximize revenue, Rajiv should charge 30 per admission in Market A and 12 per admission in Market B. At these prices, he will sell a total quantity of 24 admission tickets per day. Complete the following table by calculating Rajiv's total revenue from selling in both markets under the nondiscriminatory as well as the discriminatory price policy. Pricing Policy Total Revenue (Dollars) Nondiscriminatory Discriminatory
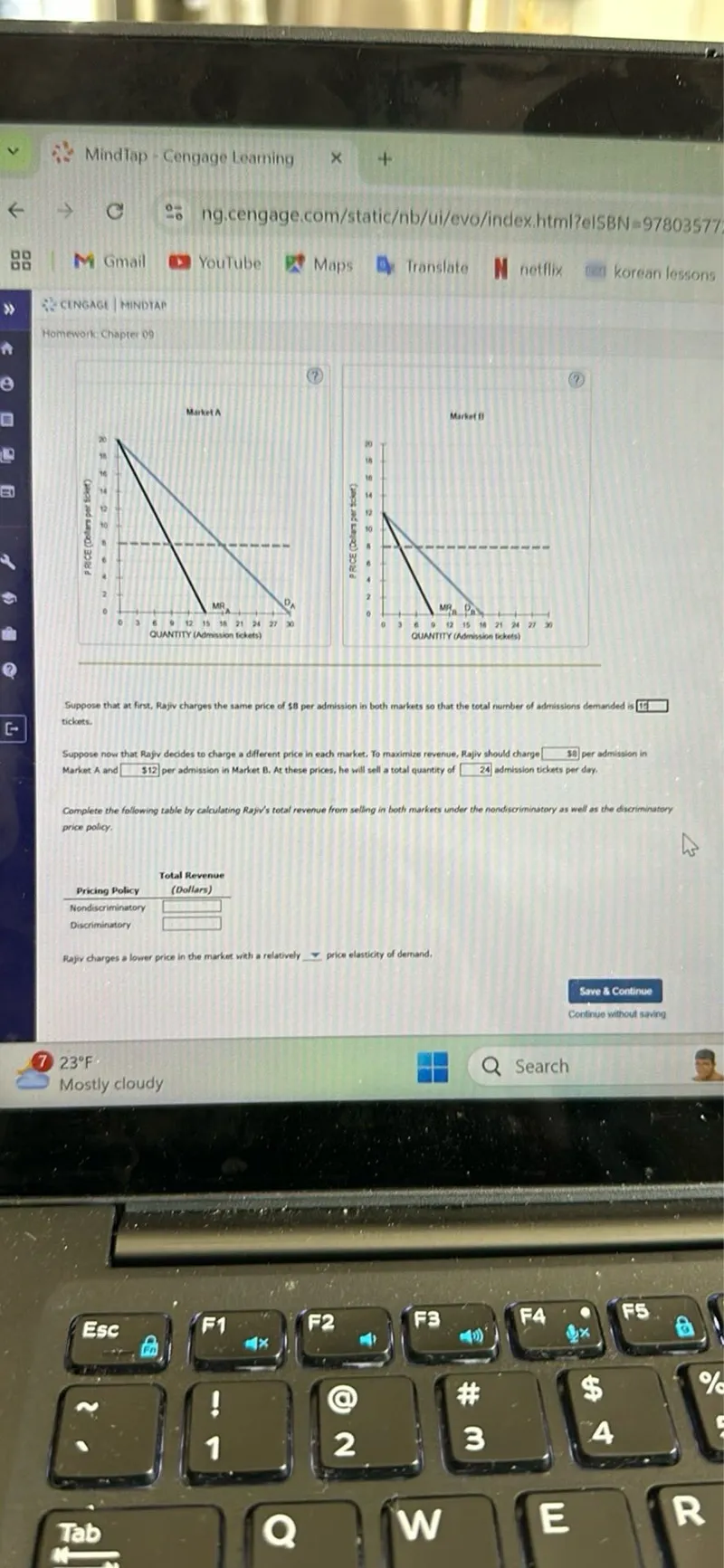
Transcript text: Suppose that at first, Rajiv charges the same price of $\$ 8$ per admission in both markets so that the total number of admissions demanded is 9 tickets.
Suppose now that Rajiv decides to charge a different price in each market. To maximize revenue, Rajiv should charge $\quad 30$ per admission in Market A and $\$ 12$ per admission in Market B. At these prices, he will sell a total quantity of 24 admission tickets per day.
Complete the following table by calculating Rajiv's total revenue from selling in both markets under the nondiscriminatory as well as the discriminatory price policy.
\begin{tabular}{lc}
Pricing Policy & \begin{tabular}{c}
Total Revenue \\
(Dollars)
\end{tabular} \\
\hline \begin{tabular}{lc}
Nondiscriminatory & $\square$ \\
Discriminatory & $\square$
\end{tabular}
\end{tabular}





