Questions: Let f be defined by f(x)= 4x+m, x<2 -6x^2+2m, x >= 2 (a) Find (in terms of m ): lim x->2+ f(x)=2m-24 (b) Find (in terms of m ): lim x->2- f(x)=m+8 (c) Find all values of m such that lim x->2- f(x)=lim x->2+ f(x) Values of m= DNE
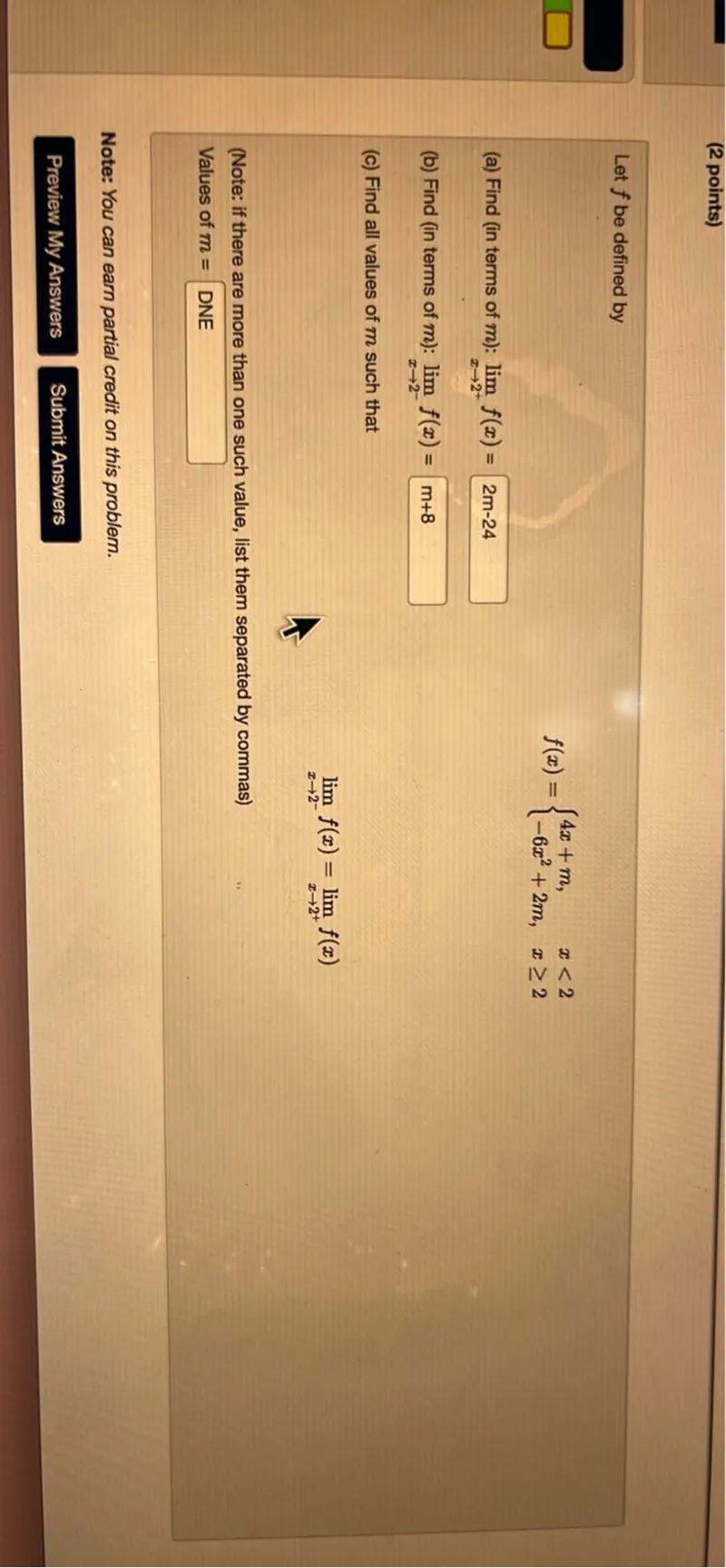
Transcript text: Let $f$ be defined by
\[
f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
4 x+m, & x<2 \\
-6 x^{2}+2 m, & x \geq 2
\end{array}\right.
\]
(a) Find (in terms of $m$ ): $\lim _{x \rightarrow 2^{+}} f(x)=2 m-24$
(b) Find (in terms of $m$ ): $\lim _{x \rightarrow 2^{-}} f(x)=m+8$
(c) Find all values of $m$ such that
\[
\lim _{x \rightarrow 2^{-}} f(x)=\lim _{x \rightarrow 2^{+}} f(x)
\]
(Note: if there are more than one such value, list them separated by commas)
\[
\text { Values of } m=
\]
$\square$ DNE





