Questions: This double bar graph shows day lengths for two cities, Blueville and Red City. Which two statements are most useful in explaining the data for both cities? Select the two correct answers. Earth moves slightly closer and farther away from the sun during its orbit. The moon completes one orbit around Earth every month. Earth rotates on a tilted axis. Earth's atmosphere can make the sun appear either larger or smaller. Earth completes one orbit around the sun every year. Average Hours of Daylight for Two Cities
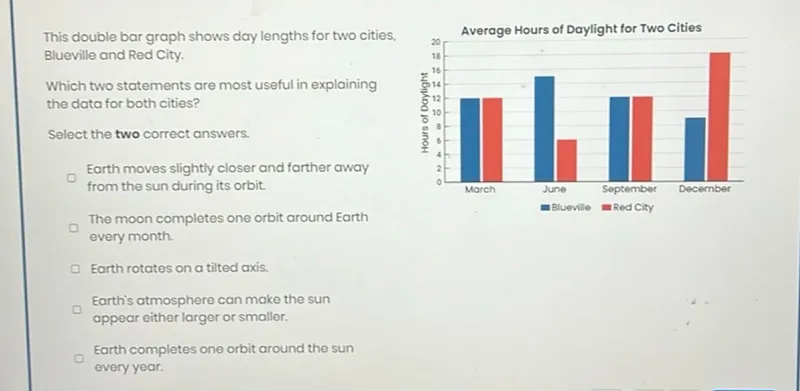
Transcript text: This double bar graph shows day lengths for two cities, Blueville and Red City.
Which two statements are most useful in explaining the data for both cities?
Select the two correct answers.
Earth moves slightly closer and farther away from the sun during its orbit.
The moon completes one orbit around Earth every month.
Earth rotates on a tilted axis.
Earth's atmosphere can make the sun appear either larger or smaller.
Earth completes one orbit around the sun every year.
Average Hours of Daylight for Two Cities





