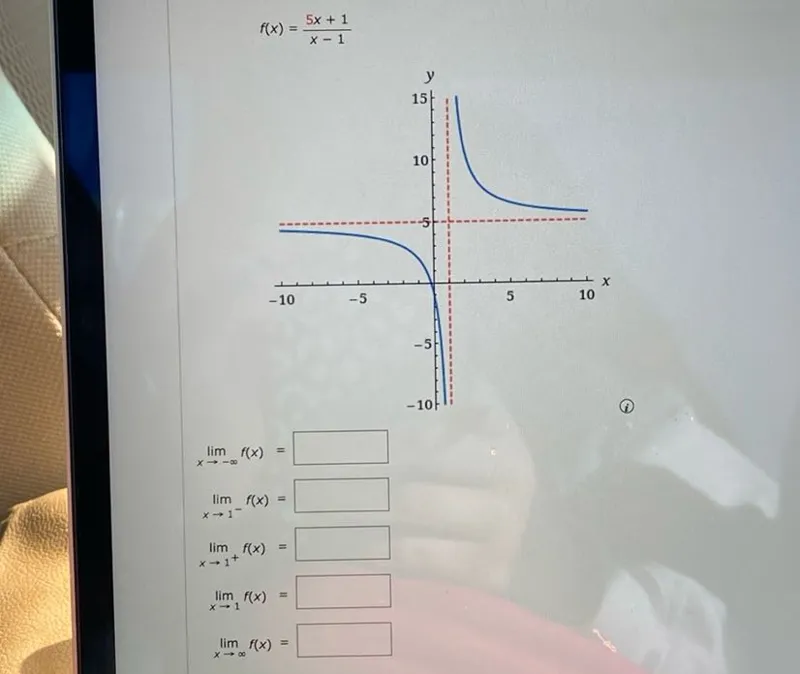
Questions: f(x)=(5x+1)/(x-1) lim x→-∞ f(x) =□ lim x→1⁻ f(x) =□ lim x→1⁺ f(x) =□ lim x→∞ f(x) =□
Transcript text: \[
f(x)=\frac{5 x+1}{x-1}
\]
\[
\begin{aligned}
\lim _{x \rightarrow-\infty} f(x) & =\square \\
\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{-}} f(x) & =\square \\
\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{+}} f(x) & =\square \\
\lim _{x \rightarrow \infty} f(x) & =\square
\end{aligned}
\]





