Questions: Use the graph of f to state the value of each quantity, If it exists. If infinite, specify e a. lim x -> -4^- f(x) = □ b. lim x -> -2 f(x) = □ c. f(-2) = □ d. lim x -> 1^+ f(x) = □ e. lim x -> -1 f(x) = □ f. lim x -> 3^- f(x) = □ g. lim x -> 3^+ f(x) = □ h. f(3) = □ i. lim x -> -∞ f(x) = □ j. lim x -> ∞ f(x) = □
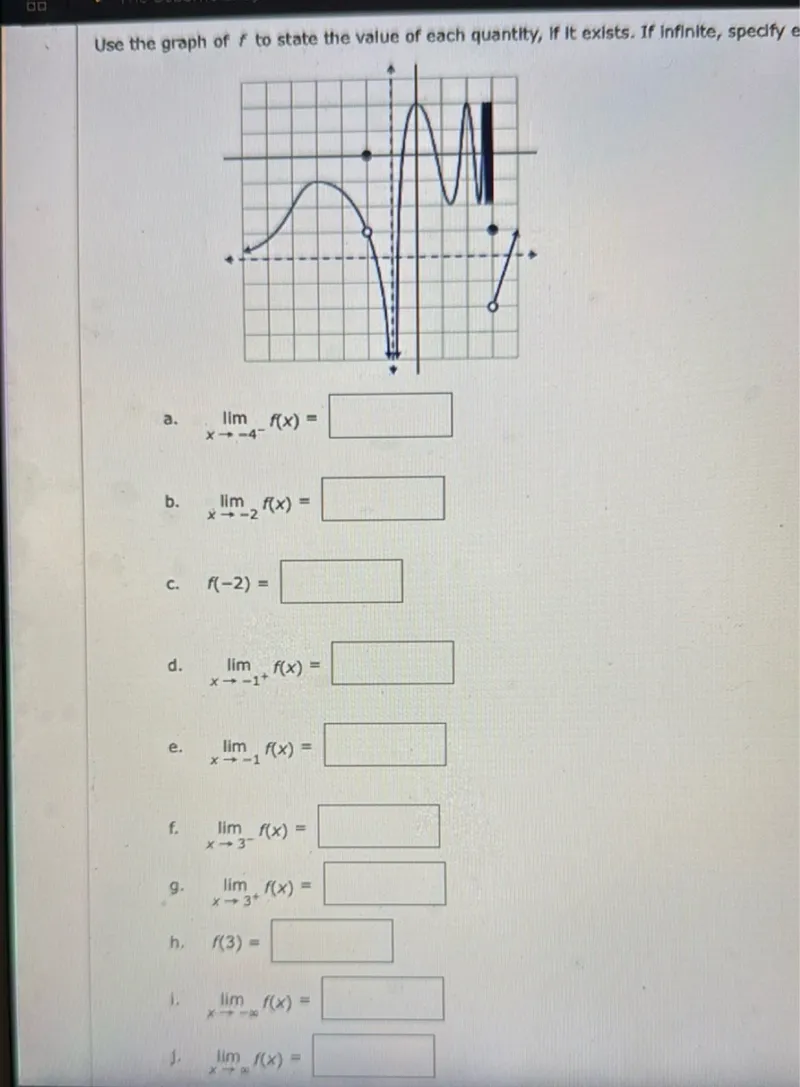
Transcript text: Use the graph of $f$ to state the value of each quantity, If it exists. If infinite, spedify e
a. $\lim _{x \rightarrow-4^{-}} f(x)=$ $\square$
b. $\quad \lim _{x \rightarrow-2} f(x)=$ $\square$
c. $f(-2)=$ $\square$
d. $\lim _{x \rightarrow-1^{+}} f(x)=$ $\square$
e. $\lim _{x \rightarrow-1} f(x)=$ $\square$
f. $\lim _{x \rightarrow 3^{-}} f(x)=$ $\square$
g. $\lim _{x \rightarrow 3^{+}} f(x)=$ $\square$
h. $f(3)=$ $\square$
i. $\lim _{x \rightarrow-\infty} f(x)=$ $\square$
j. $\lim _{x \rightarrow \infty} f(x)=$ $\square$





