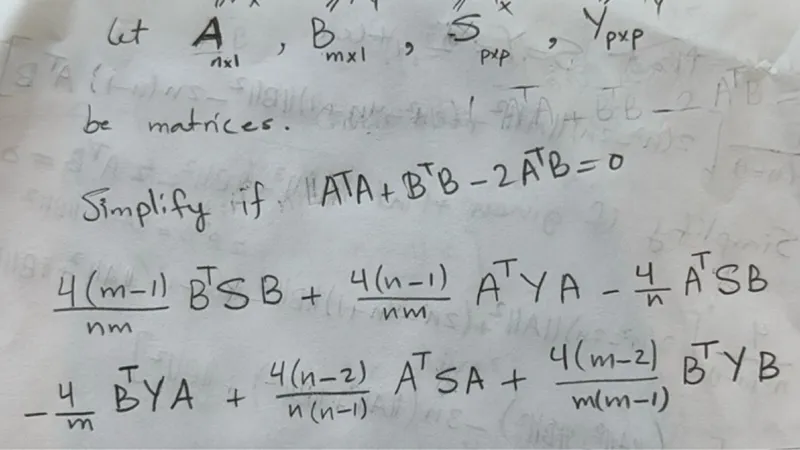△
Simplify the given matrix expression under the condition \( A^{\top} A + B^{\top} B - 2 A^{\top} B = 0 \).
○
Analyze the condition \( A^{\top} A + B^{\top} B - 2 A^{\top} B = 0 \).
☼
Rewriting the condition:
\[
A^{\top} A + B^{\top} B - 2 A^{\top} B = 0 \implies (A - B)^{\top}(A - B) = 0 \implies \|A - B\|^2 = 0.
\]
This implies \( A = B \).
✧
The condition implies \( A = B \).
△
Substitute \( A = B \) into the given expression and simplify.
○
Substitute \( A = B \) into the expression.
☼
The original expression is:
\[
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{4(m-1)}{n m} B^{\top} S B + \frac{4(n-1)}{n m} A^{\top} Y A - \frac{4}{n} A^{\top} S B \\
- & \frac{4}{m} B^{\top} Y A + \frac{4(n-2)}{n(n-1)} A^{\top} S A + \frac{4(m-2)}{m(m-1)} B^{\top} Y B.
\end{aligned}
\]
Substituting \( A = B \), we get:
\[
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{4(m-1)}{n m} B^{\top} S B + \frac{4(n-1)}{n m} B^{\top} Y B - \frac{4}{n} B^{\top} S B \\
- & \frac{4}{m} B^{\top} Y B + \frac{4(n-2)}{n(n-1)} B^{\top} S B + \frac{4(m-2)}{m(m-1)} B^{\top} Y B.
\end{aligned}
\]
✧
The expression after substitution is:
\[
\begin{aligned}
& B^{\top} S B \left( \frac{4(m-1)}{n m} - \frac{4}{n} + \frac{4(n-2)}{n(n-1)} \right) \\
- & B^{\top} Y B \left( \frac{4(n-1)}{n m} - \frac{4}{m} + \frac{4(m-2)}{m(m-1)} \right).
\end{aligned}
\]
△
Simplify the coefficients of \( B^{\top} S B \) and \( B^{\top} Y B \).
○
Simplify the coefficient of \( B^{\top} S B \).
☼
The coefficient of \( B^{\top} S B \) is:
\[
\frac{4(m-1)}{n m} - \frac{4}{n} + \frac{4(n-2)}{n(n-1)}.
\]
Simplifying:
\[
\frac{4(m-1)}{n m} - \frac{4}{n} + \frac{4(n-2)}{n(n-1)} = \frac{4(mn - m - n + 1)}{n m (n-1)}.
\]
✧
The coefficient of \( B^{\top} S B \) is \( \frac{4(mn - m - n + 1)}{n m (n-1)} \).
○
Simplify the coefficient of \( B^{\top} Y B \).
☼
The coefficient of \( B^{\top} Y B \) is:
\[
\frac{4(n-1)}{n m} - \frac{4}{m} + \frac{4(m-2)}{m(m-1)}.
\]
Simplifying:
\[
\frac{4(n-1)}{n m} - \frac{4}{m} + \frac{4(m-2)}{m(m-1)} = \frac{4(nm - n - m + 1)}{n m (m-1)}.
\]
✧
The coefficient of \( B^{\top} Y B \) is \( \frac{4(nm - n - m + 1)}{n m (m-1)} \).
△
Analyze special cases for \( n \) and \( m \).
○
Case: \( n = m \).
☼
If \( n = m \), the coefficients of \( B^{\top} S B \) and \( B^{\top} Y B \) become:
\[
\frac{4(n^2 - 3n + 1)}{n^2(n-1)}.
\]
The expression simplifies to:
\[
\frac{4(n^2 - 3n + 1)}{n^2(n-1)} B^{\top} (S + Y) B.
\]
✧
If \( n = m \), the expression is \( \frac{4(n^2 - 3n + 1)}{n^2(n-1)} B^{\top} (S + Y) B \).
○
Case: \( n = m = 1 \).
☼
If \( n = m = 1 \), \( A \) and \( B \) are scalars, and \( S \) and \( Y \) are scalars. The expression becomes:
\[
-4 A^2 (S + Y).
\]
✧
If \( n = m = 1 \), the expression is \( -4 A^2 (S + Y) \).
○
Case: \( n = m = 2 \).
☼
If \( n = m = 2 \), the coefficients of \( B^{\top} S B \) and \( B^{\top} Y B \) are both \( -1 \). The expression simplifies to:
\[
-B^{\top} (S + Y) B.
\]
✧
If \( n = m = 2 \), the expression is \( -B^{\top} (S + Y) B \).
○
Case: \( n \neq m \).
☼
If \( n \neq m \), the coefficients cannot be further simplified without additional information. The expression remains:
\[
B^{\top} S B \cdot \frac{4(mn - m - n + 1)}{n m (n-1)} + B^{\top} Y B \cdot \frac{4(nm - n - m + 1)}{n m (m-1)}.
\]
✧
If \( n \neq m \), the expression cannot be simplified further.
△
Summarize the results for specific cases.
○
Summarize results.
☼
- If \( n = m \), the expression is \( \frac{4(n^2 - 3n + 1)}{n^2(n-1)} B^{\top} (S + Y) B \).
- If \( n = m = 1 \), the expression is \( -4 A^2 (S + Y) \).
- If \( n = m = 2 \), the expression is \( -B^{\top} (S + Y) B \).
- If \( n \neq m \), the expression cannot be simplified further.
✧
The simplified expression depends on the relationship between \( n \) and \( m \).
☺0